 |
|
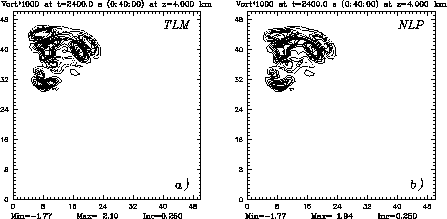
Figure 2:
x-y slices (at z = 4.0 km) of (a) tangent linear perturbation
and (b) nonlinear perturbation in vorticity at t = 40 min for a 1 %
perturbation in initial water vapor (in |
Before we proceed to the sensitivity computation, we validate the TLM solutions computed by the ADIFOR-generated code, which describe the linear evolution of perturbations. The validation is carried out by comparison with the nonlinear perturbation (NLP) fields; the difference fields computed between the nonlinear control run and another nonlinear run whose initial state is slightly perturbed from it.
Figure 2 shows the TLM and NLP fields of vorticity at 40 min for a
1% perturbation (bias-type) in water vapor over the whole model domain
except for the lateral, top, and bottom boundaries. They are plotted on
an x-y plane at z = 4.0 km.
 |
|
Figure 2:
x-y slices (at z = 4.0 km) of (a) tangent linear perturbation
and (b) nonlinear perturbation in vorticity at t = 40 min for a 1 %
perturbation in initial water vapor (in |